Wastewater Mechanical Seals Ensuring Pump Reliability Against Corrosion

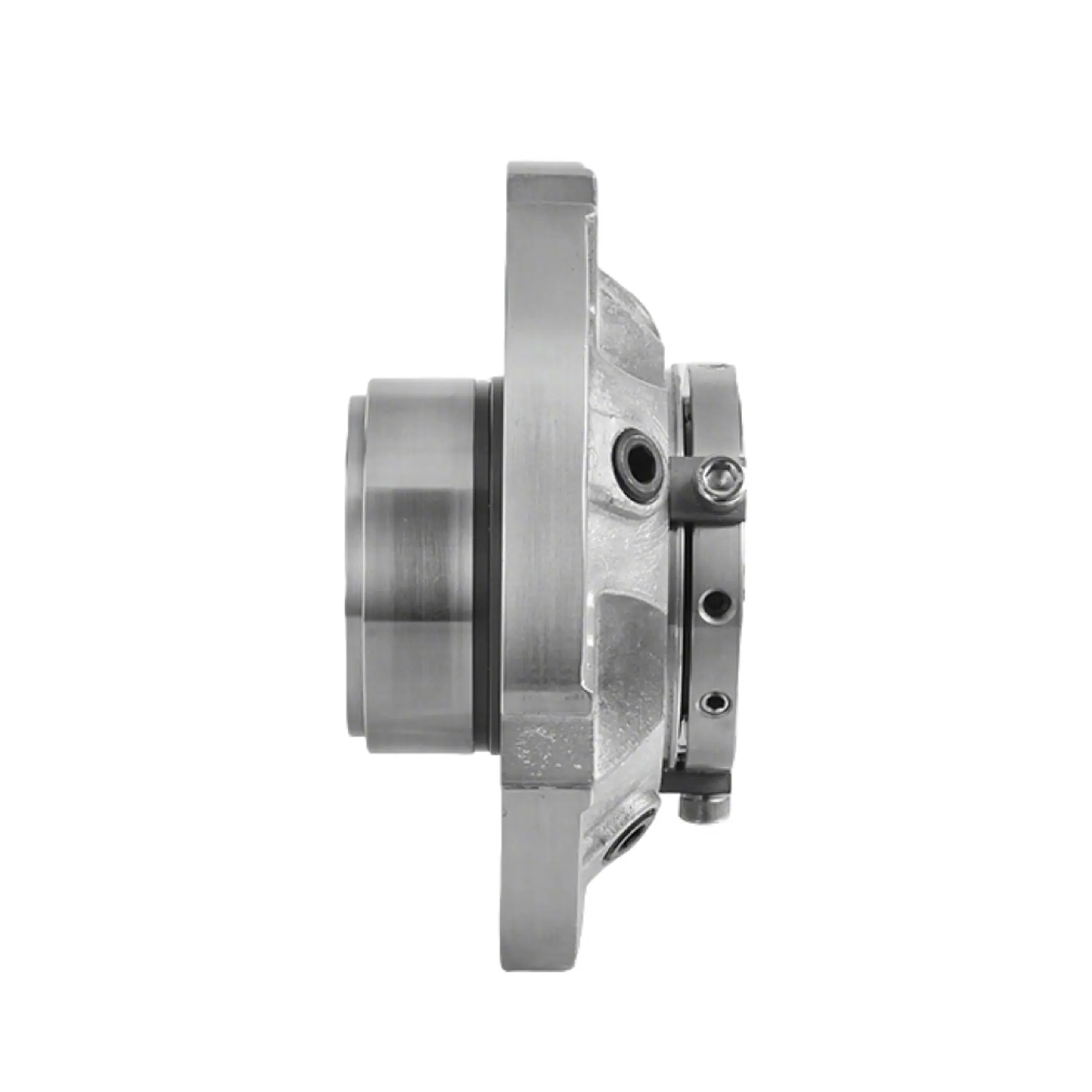
Reliable wastewater mechanical seals are critical for pump longevity in corrosive environments. They form the primary barrier, preventing abrasive and corrosive wastewater from damaging pump bearings and other internal components. This directly ensures operational continuity and reduces maintenance costs. For example, a water treatment facility achieved a 30% reduction in maintenance costs by implementing mechanical seals. GW SEAL provides high-performance wastewater mechanical seal solutions, essential for protecting equipment and minimizing downtime.
Key Takeaways
- Wastewater mechanical seals protect pumps from harsh wastewater. They stop corrosive liquids and abrasive particles from damaging pump parts. This helps pumps last longer and reduces repair costs.
- Choosing the right materials for seals is very important. Materials like silicon carbide and tungsten carbide resist corrosion and wear. These materials help seals work well in tough wastewater conditions.
- Good design features make seals even better. Double seals use a clean liquid to protect the pump. Special designs also stop solids from clogging the seal. These features make seals more reliable and last longer.
The Corrosive Challenge in Wastewater Treatment

Understanding Wastewater's Corrosive Nature
Wastewater presents a significant corrosive challenge to treatment infrastructure. Its complex composition includes various chemical components and fluctuating pH levels. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S), produced by sulfate-reducing bacteria, is a major contributor. This H2S later oxidizes into sulfuric acid, which drastically lowers pH and corrodes concrete. Other elements like dissolved oxygen, chlorides, carbon dioxide, calcium, and ammonia also contribute to its aggressive nature. While natural waters typically have a pH between 4.5 and 8.5, corrosive wastewater environments often see a significant pH drop due to sulfuric acid formation.
Impact of Corrosion on Pump Reliability
Corrosion severely impacts pump reliability in wastewater systems, leading to various failure modes. Pitting corrosion frequently occurs when protective layers on carbon steel or cast-iron alloys break down, creating localized areas of deep corrosion. Stainless steel also experiences pitting, especially with high chloride levels or in oxygen-depleted zones. Galvanic corrosion happens when dissimilar metals connect in an electrolyte, causing the less noble metal to corrode. Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion (MIC) is also common; bacteria produce acids that accelerate material degradation. These corrosive actions directly cause pump failures. Pumps often experience leaks as components weaken. Corrosion also reduces the structural integrity of parts, leading to weakened components. Impeller damage and wear, a direct result of corrosion, cause reduced flow, increased vibration, and noise. These issues compromise operational efficiency and demand frequent maintenance.
How Wastewater Mechanical Seals Combat Corrosion

Material Selection for Corrosion Resistance in Wastewater Mechanical Seals
Selecting the right materials is paramount for wastewater mechanical seals. These materials must withstand the aggressive chemical attack of wastewater. For seal faces, specific materials offer superior resistance. Direct Sintered Silicon Carbide provides excellent chemical resistance for almost any application. It contains no free silicon metal. General Silicon Carbide is also a common choice. It offers high thermal conductivity, abrasion resistance, and chemical resistance. Diamond Coating on Silicon Carbide further enhances hardness and performance. This coating benefits low lubrication or dry-running applications. Nickel-Bound Tungsten Carbide presents a strong alternative. It offers broader chemical resistance than cobalt-bound versions. This material is less fragile than silicon carbide. Acid-Grade Carbon Graphite can also serve in highly corrosive applications. It lacks resin filler.
Other components of the wastewater mechanical seal also require careful material consideration.
| Material | Property | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Silicon Carbide | Corrosion Resistance | Excellent corrosion resistance to most chemicals. |
| Tungsten Carbide | Corrosion Resistance | Good corrosion resistance, but not as broad as silicon carbide. |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosion Resistance | Good corrosion resistance in many environments. |
| Special Alloys (e.g., Hastelloy, Monel) | Corrosion Resistance | Excellent corrosion resistance in highly aggressive chemical environments. |
| PTFE | Chemical Resistance | Excellent chemical resistance to almost all chemicals. |
These materials ensure the seal's longevity and effectiveness. Some designs even feature no wetted metal components. This approach is ideal for highly corrosive services. It avoids the need for expensive premium metal grades. For example, the AST50 Multi-Spring Component Outside Seal has no metal parts in contact with the fluid, making it suitable for non-metallic pumps. The AST Dual Cartridge Seal with SC/SC (Silicon Carbide) hard faces also provides robust protection in challenging applications.
Design Features for Enhanced Corrosion Protection
Beyond material selection, specific design features significantly enhance corrosion protection for wastewater mechanical seals. Balanced seal designs reduce the net closing force on the seal faces. This allows for better lubrication. It also leads to lower heat generation, reduced face wear, and decreased power consumption. Balanced seals handle higher pressures effectively. Protected springs represent another critical design element. Placing springs on the atmospheric side of the seal prevents contact with the process fluid. This protects them from clogging by dirt and debris. It ensures the springs can respond to movements and vibrations. This keeps the seal faces closed and prevents premature failure.
Double mechanical seals, also known as tandem seals, are often preferred in wastewater applications. They introduce a clean barrier fluid between two seal faces. This prevents direct contact between the wastewater and the outer seal. This design significantly enhances seal life and reliability. Furthermore, manufacturers use corrosion-resistant materials for the seal's structural components. Materials like stainless steel (304 or 316) and titanium offer excellent protection against harsh chemicals. For instance, 316 stainless steel casting proves effective in heavy-duty applications. Hard face materials such as silicon carbide are also recommended. They provide exceptional wear resistance and thermal conductivity against abrasive particles like sand in wastewater. Silicon carbide offers significantly higher resistance to corrosion, wear, and heat compared to tungsten carbide.
Key Features of Reliable Wastewater Mechanical Seals
Advanced Face Materials for Harsh Environments
Reliable wastewater mechanical seals depend on advanced face materials. These materials must withstand the harsh, abrasive, and corrosive conditions found in wastewater. Silicon carbide and tungsten carbide are primary choices for these demanding applications. Silicon carbide offers extreme hardness, wear, and corrosion resistance. It performs well in abrasive and chemically aggressive environments. Industries like chemical processing, mining, and power generation use it often. However, silicon carbide can be costly and brittle.
Tungsten carbide generally surpasses silicon carbide in hardness and wear resistance. This makes tungsten carbide an optimal solution for seals exposed to severe abrasive conditions. It offers toughness and withstands impact and abrasion. Wastewater, oil and gas, and slurry pump applications frequently use tungsten carbide. It delivers durability and wear resistance under heavy mechanical stress. However, tungsten carbide can corrode in acidic environments.
-
Silicon Carbide:
- Highly effective in abrasive and chemically aggressive environments.
- Offers extreme hardness, wear, and corrosion resistance.
- Ideal for industries like chemical processing, mining, and power generation.
- Drawbacks include higher cost and brittleness.
-
Tungsten Carbide:
- Valued for its toughness and ability to withstand impact and abrasion.
- Frequently used in oil and gas, wastewater, and slurry pump applications.
- Delivers durability and wear resistance under heavy mechanical stress.
- Can corrode in acidic environments.
Robust Elastomers and Secondary Seals
Elastomers and secondary seals play a vital role in maintaining the integrity of wastewater mechanical seals. They provide flexibility and chemical resistance. EPDM rubber is a common choice for wastewater applications. It shows excellent resistance to wastewater, distilled water, and cold water. FKM (Viton®) is another elastomer, but it has limited resistance to water and steam. FKM is better suited for chemicals, fuels, and high temperatures.
| Property | EPDM Rubber | FKM (Viton®) |
|---|---|---|
| Water/Steam Resistance | Excellent | Limited |
| Recommended Use | Outdoor and water-based | Chemicals, fuels, high temperatures |
Secondary seals, such as O-rings and bellows, provide additional barriers against fluid leakage. They ensure a tight seal even under extreme conditions.
-
Elastomeric Bellows Seals:
- Offer excellent flexibility.
- Suitable for applications with varying temperature and pressure conditions.
- Elastomers like nitrile rubber and fluorocarbon provide flexibility, resilience, and resistance to certain chemicals.
- Accommodate shaft misalignment well in dynamic applications.
-
Metal Bellows Seals:
- Known for their durability.
- Ideal for high-temperature or high-pressure scenarios.
- Superior resistance to chemical attack in harsh chemical environments.
- Significantly reduces the risk of leakage and contamination.
- Minimizes the need for frequent seal replacements and maintenance.
- Offers resilience and durability to withstand challenging conditions in wastewater treatment pumps.
- Typical materials like stainless steel (316, 316L) are corrosion resistant.
- Ni-Cr-Mo alloy performs excellently in aggressive chemical environments.
-
O-rings:
- Offer simplicity in installation and versatility.
- Can be a cost-effective sealing alternative.
- Available in various elastomeric compounds for different performance capabilities.
- Come in different durometers to tailor seal design for specific applications.
Non-Clogging and Self-Cleaning Designs
Wastewater contains solids and particulate matter. This makes non-clogging and self-cleaning designs essential for mechanical seals. These designs prevent solid accumulation and maintain seal integrity. Some seals incorporate a compression ring. This ring generates movement around the dynamic O-ring. This action effectively reduces the accumulation of solids. Other designs isolate springs from the process fluid. This significantly reduces the potential for clogging.
💡 Tip: Seal flushing is a critical method in abrasive environments. It prevents the buildup of particulate matter, thereby maintaining seal integrity.
Gorman-Rupp seals, for example, are known for their use in municipal water and wastewater treatment. They emphasize the need for corrosion-resistant and clog-resistant designs. These features ensure continuous operation and minimize downtime in challenging wastewater applications.
- Specific designs incorporate a compression ring. This ring generates movement around the dynamic O-ring. It effectively reduces the accumulation of solids.
- Other designs isolate springs from the process fluid. This significantly reduces the potential for clogging.
- Seal flushing is a critical method in abrasive environments. It prevents the buildup of particulate matter. This maintains seal integrity.
Selecting the Right Wastewater Mechanical Seal for Your Application
Choosing the correct wastewater mechanical seal is crucial for pump reliability and longevity. This selection process requires a thorough understanding of the application's specific demands.
Assessing Wastewater Characteristics
Engineers must first assess the wastewater's characteristics. This includes physical, chemical, and biological properties. Physical characteristics include turbidity, color, odor, total solids, and temperature. For example, elevated temperatures can negatively impact aquatic organisms and reduce oxygen levels. Chemical characteristics involve pH value, dissolved oxygen concentrations, Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD), Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD), nitrogen, phosphorus, chlorides, sulfates, and heavy metals. pH directly influences material corrosion resistance. Corrosion occurs when metals react with acids, bases, or other corrosive substances. This leads to material degradation. Biological characteristics include microbial populations and oxygen required for nitrification. Solids content, whether dissolved, suspended, or settled, also impacts seal choice. Selecting seal materials that resist the specific chemicals and abrasive particles in the wastewater is essential.
Considering Pump Operating Conditions
Pump operating conditions significantly influence mechanical seal performance and longevity. These conditions include temperature, pressure, and speed. High temperatures may necessitate seals designed for extreme heat. Corrosive fluids require resistant materials. The pump shaft's speed is also crucial. High shaft speeds generate heat and friction. This requires seals with enhanced heat dissipation. High-pressure applications demand robust seal designs capable of withstanding fluid forces. Changes in pressure, temperature, or speed directly influence a mechanical seal's leak rate. This indicates its responsiveness to transient operating conditions.
Consulting with Seal Experts
Consulting with seal experts is a vital step. They offer specialized knowledge for complex applications. Experts can help interpret wastewater characteristics and operating conditions. They recommend the most suitable seal materials and designs. This ensures optimal performance and extends the seal's service life.
Investing in high-quality, corrosion-resistant wastewater mechanical seals is paramount for ensuring the reliability and longevity of wastewater treatment pumps. These seals directly combat the challenges posed by corrosive environments, leading to significant operational savings and reduced downtime. Such investments often yield a return within a year, driven by energy savings and prevented shutdowns. Prioritizing robust sealing solutions enhances overall reliability and reduces operational costs, protecting critical infrastructure.
FAQ
What is the primary function of wastewater mechanical seals?
Wastewater mechanical seals form a critical barrier. This barrier prevents corrosive and abrasive wastewater from damaging pump components. This ensures continuous operation and reduces maintenance.
Which materials offer the best corrosion resistance for wastewater mechanical seals?
Silicon carbide and tungsten carbide are top choices. They provide excellent resistance to harsh chemicals and abrasive particles. Special alloys also offer superior protection.
How do double mechanical seals improve pump reliability in wastewater applications?
Double seals use a clean barrier fluid. This fluid separates the wastewater from the outer seal. This design significantly extends seal life and enhances reliability.